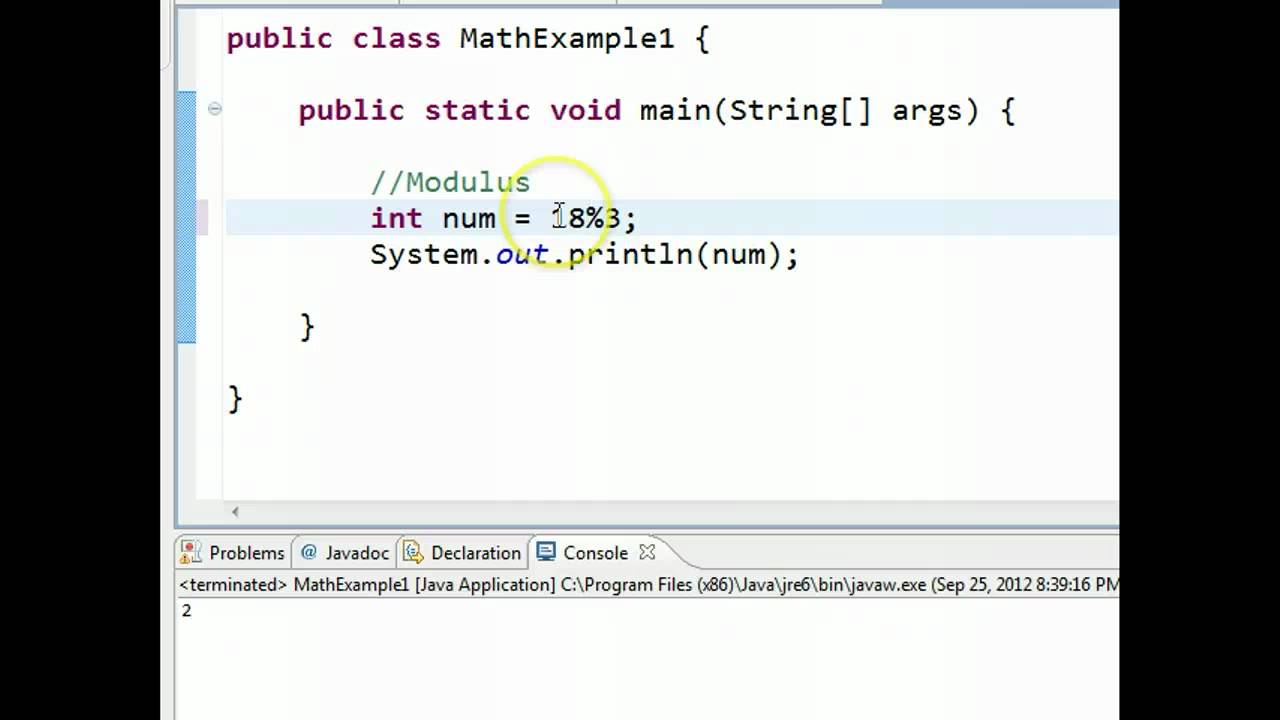
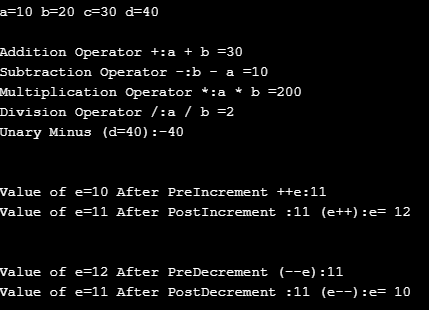
The Java modulus '%' operator is one of numerous operators built into the Java programming language The operator is used to calculate the remainder of the division between two numbers First, let us discuss how the operator worksHow Operators Work in Java An operator in Java is a special symbol or keyword that's used to designate a mathematical operation or some other type of operation that can be performed on one or more values, called operands In all, Java has about 40 operators This section focuses on the operators that do basic arithmetic//This is same as i = i8;
Java Programming Integer Division And The Modulus Operator The Seeker S Quill
Java modulus operator explained
Java modulus operator explained-Would result in the remainder of 2 being stored in the variable resultOfModIf we do c = a % b;




Eqczss334iamym
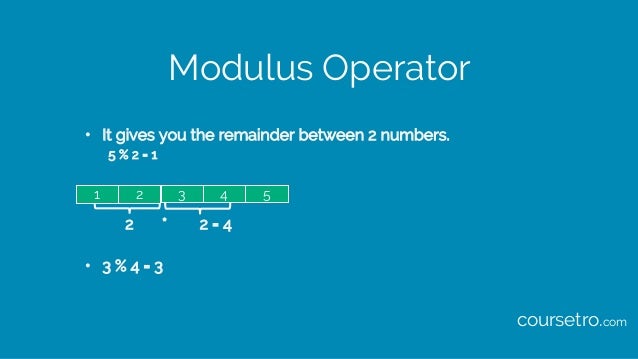
The Remainder or Modulus Operator in Java Java has one important arithmetical operator you may not be familiar with, %, also known as the modulus or remainder operatorThe % operator returns the remainder of two numbers For instance 10 % 3 is 1 because 10 divided by 3 leaves a remainder of 1 You can use % just as you might use any other more common operatorIn general, Percent sign(%) acts as a modulus operator in java programming language Modulus operator is an operator that works on integers and yields the remainder when one number is divided by another Thus x = A%B means that x will carry the va Appendix A Operator Precedence in Java Java has welldefined rules for specifying the order in which the operators in an expression are evaluated when the expression has several operators For example, multiplication and division have a higher precedence than addition and subtraction Precedence rules can be overridden by explicit parentheses
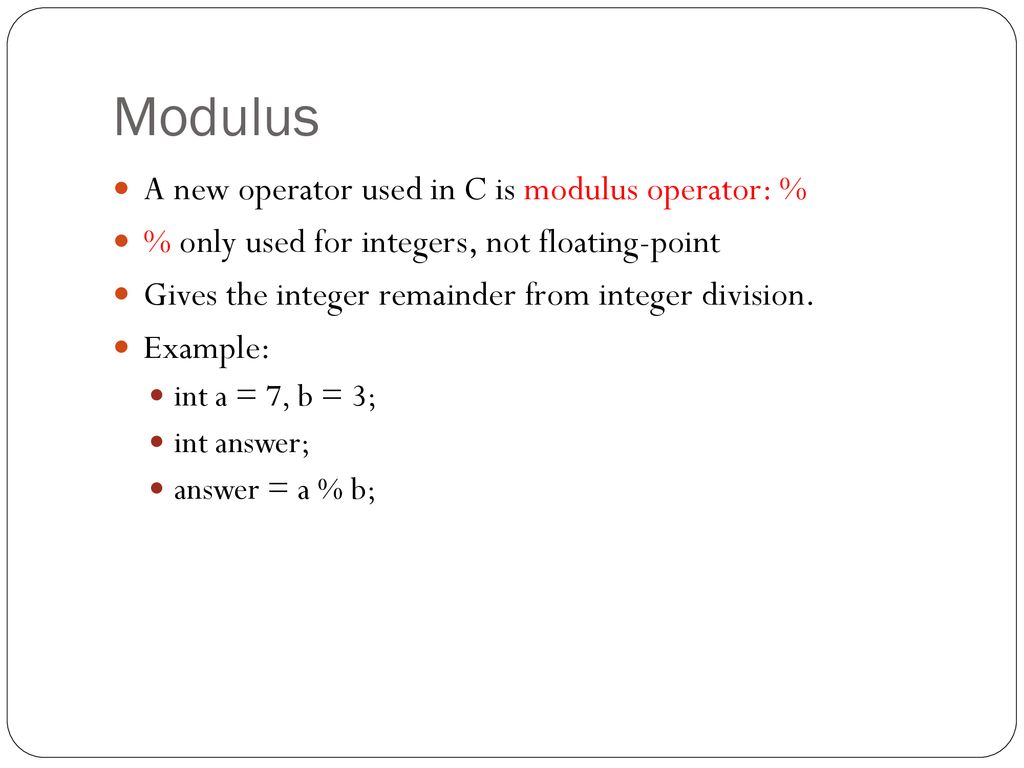
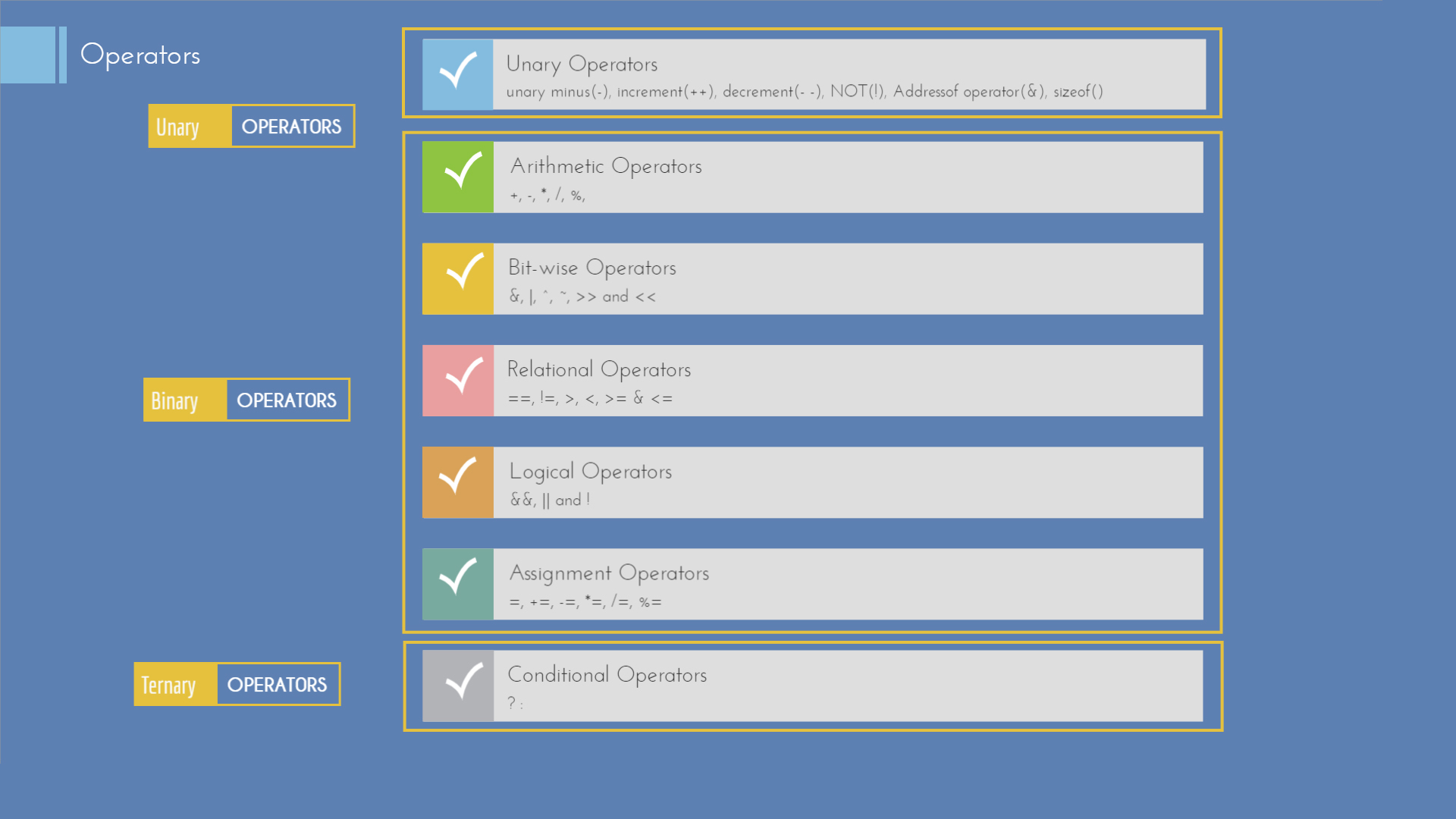
The binary to decimal conversion process is a reverse process to the one previously explained So this time, it involves multiplication and addition instead of division For example, 5748 in decimal is equivalent to (5×1000) (7×100) (4×10) (8×1), where 1000 is equivalent to 10 3 , 100 is equivalent to 10 2 , 10 is equivalent to 10 1The = is called the addition assignment operator Other shorthand operators are shown below table OperatorJava Modulo operator or modulus operator is used to getting the remainder when we divide an integer with another integer Table of Contents show Java Modulo Operator Syntax The % character is the modulus operator in Java
Operators in Java Operator in Java is a symbol that is used to perform operations For example , , *, / etc There are many types of operators in Java which are given below Unary Operator, Arithmetic Operator, Shift Operator, Relational Operator, Bitwise Operator, Logical Operator, Ternary Operator and ;/* * Modulus operator returns reminder of the devision of * floating point or integer types */Java has one important arithmetical operator you may not be familiar with, %, also known as the modulus or remainder operator The %operator returns the



Java Modulus Youtube



The Mod Function
Note In many cases, the assignment operators can be combined with other operators to build a shorter version of the statement called Compound StatementFor example, instead of a = a5, we can write a = 5 Let's look at similar assignment operators that form the compound statements "=" This operator is a compound of '' and '=' operators JavaScript provides the user with five arithmetic operators , , *, / and % The operators are for addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and remainder (or modulo), respectively AdditionSyntax a b Usage 2 3 // returns 5 true 2 // interprets true as 1 and returns 3 false 5 // interprets false as 0 and returns 5 trueJava Math Operator Precedence Once you start combining the Java math operators in math expressions it becomes important to control what calculations are to be executed when, in order to get the desired result The Java math operators have a natural operator precedence which is similar to the precedence of standard math operators




Mod Division In Java Vertex Academy



Java Operators Ternary Operator
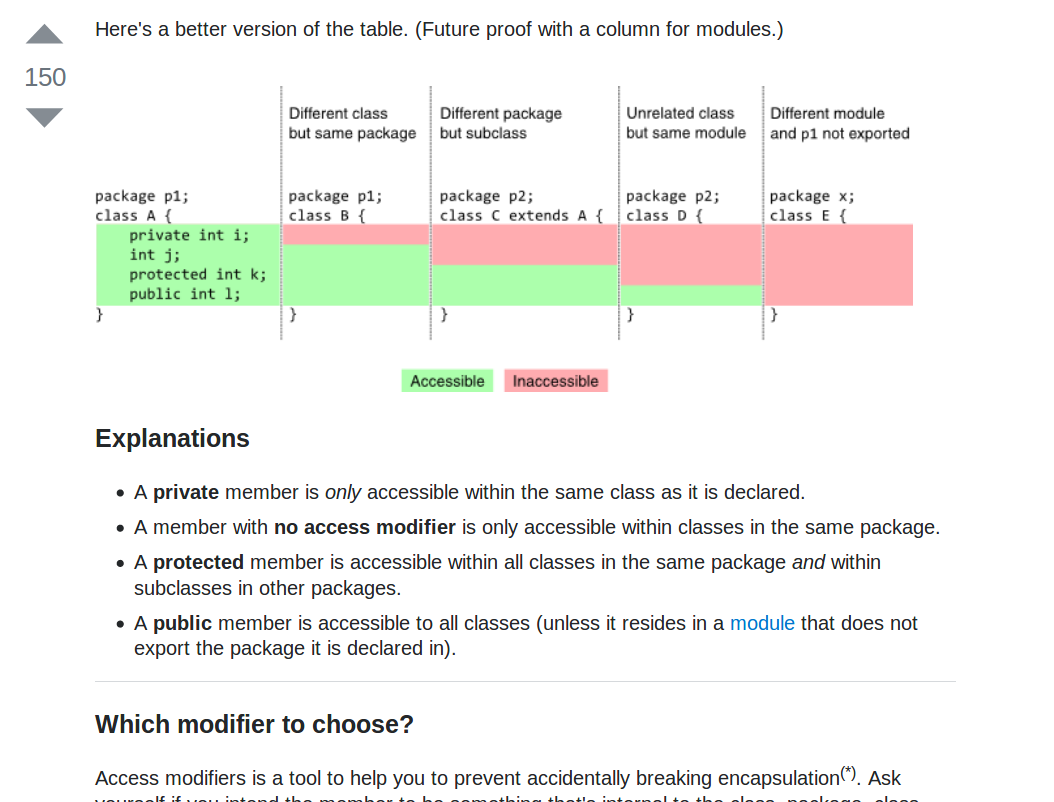
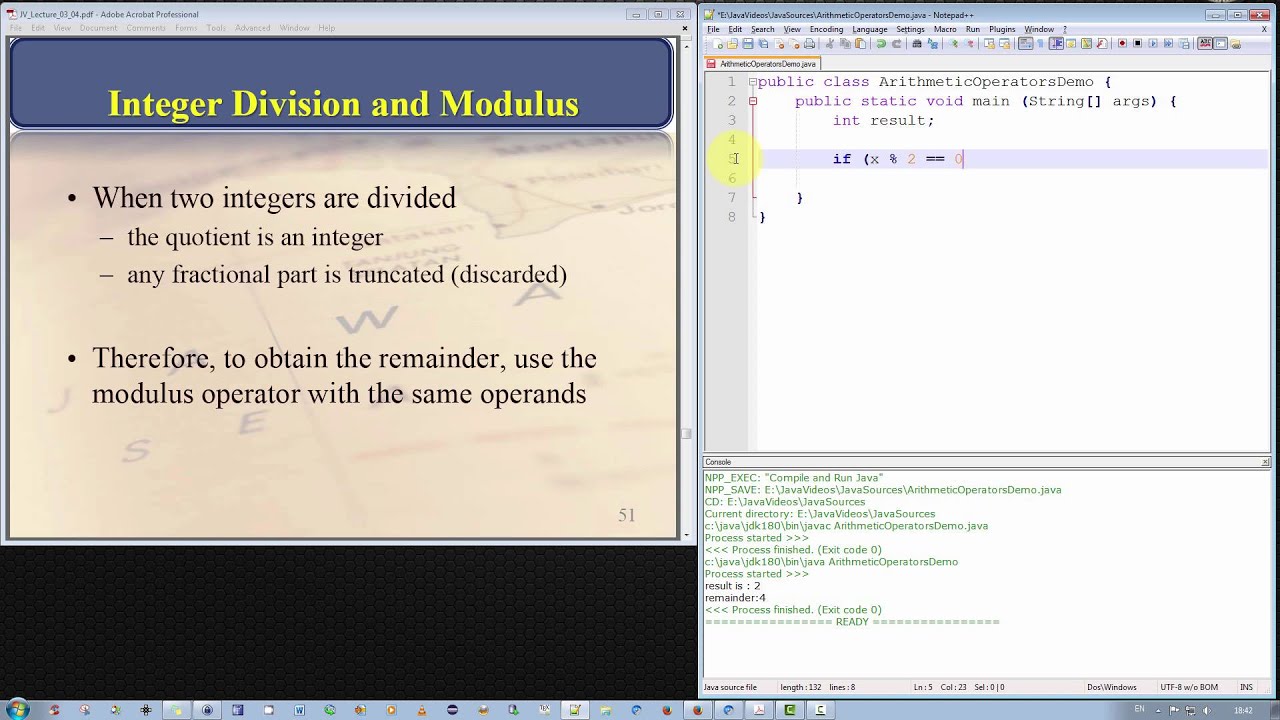
// c = 0 because 100 = 50*2 0 D = d*q r using simple maths However I felt aModulus Returns the division remainder x % y Try it » Increment Increases the value of a variable by 1 x Try it »Decrement Decreases the value of a variable by 1x Try it » Java Assignment Operators Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables In the example below, we use the assignment operator (=) The modulo operator is based on the same equations, but it uses Mathfloor () to compute quotients If both dividend and divisor are positive, the modulo operator produces the same results as the remainder operator (example 3) If, however, dividend and divisor have different signs, then the results are different (example 4)




The Modulus Operator And Its Use Array Data Structure Computing



Numbers In Ruby Ruby Study Notes Best Ruby Guide Ruby Tutorial
So there are two symbols (java operators) to get the result after divisionThe symbol " / " is used to get a quotient, and the symbol " % " is used to get a remainder These Java operators can be applied to any numeric type data as well as to char type data But these Java operators cannot be implemented to Boolean type dataAssignment Operator Java Operator Java Programming – Integer Division and the Modulus Operator Oct10 by theseekersquill I am continuing on with my video series on Java programming for beginners In this video, I discuss Integer division and the modulus operator and I explain in detail how to use them, providing many examples In my previous video on arithmetic operators, I




Python Remainder Operator 8 Examples Of Pyhton Remainder Operator




Modulus Operator Cs101 Udacity Youtube
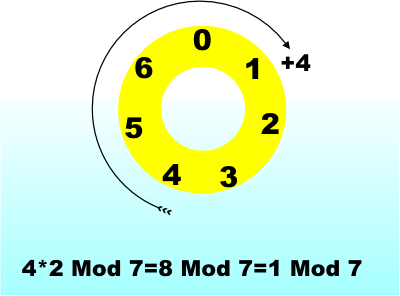
This video goes through how to apply the modulus operationJavaScript Tutorial Operators Mod Modulus (%) operator returns only the remainder If either value is a string, an attempt is made to convert the string to a number For example, the following line of code var resultOfMod = 26 % 3;1 day ago To get the modulus of two integers, Java uses the % symbol The example given in the table is similar to the algebraic expression y mod 3 The % operator gives the remainder after y is divided by 3 That is, 19%5 will evaluate to 4




Eqczss334iamym




What Is The Result Of In Python Stack Overflow
The modulus function, in programming, returns the modulo (remainder after division) of two numbers explained here The modulo of "a" divided by "b" is equal to the remainder after the division The example you provided, 3 % 7 is literally saying "the remainder when 3 is divided by 7", which is expressed incorrectlyViewed 3k times 3 Use a modulus operator is something which all programmers must to know I know it =) In java we have int a = 100 , b = 50, c;The modulus operator gives the remainder in the sense that the original value is recovered from the integer arithmatic as (num1/num2)*num2 num1%num2 == num1 This is the theoretical explanation An example (using python for ease of typing) gives >>> 21 %4 3 >>> 21 /4 6 >>> 6*4 3 21 Your Java program above would give you




Engineered For Tomorrow Unit 1 Introduction To Java




Engineered For Tomorrow Unit 1 Introduction To Java
In order to find the remainder you need to divide So you are dividing even if the result required isn't the result of the division 3%2 would have a remainder 1, yes Dave Tolls wrote 05 is not a whole number, so 1 divided by 2 is 0 remainder 1 So the modulus is 1 The Modulus Operator The modulus operator, %, returns the remainder of a division operation It can be applied to floatingpoint types as well as integer types The following example program demonstrates the % Java Code Go to the editorIn Python and generally speaking, the modulo (or modulus) is referred to the remainder from the division of the first argument to the second The symbol used to get the modulo is percentage mark ie '%' In Python, the modulo '%' operator works as follows The numbers are first converted in the common type
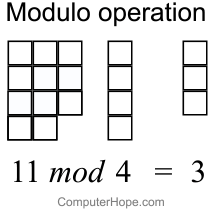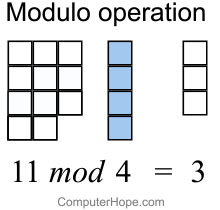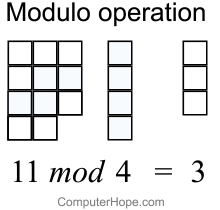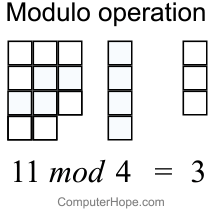



What Is Modulo




Multiplying In Java Method Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
) consists of three operands It is used to evaluate Boolean expressions The operator decides which value will be assigned to the variable modulus In Java you take the remainder with the % operator % is informally called the modulus operator, (sometimes called mod or modulo) though mathematicians and serious computer scientists would beg to differ, it is a remainder operator not a modulus The JLS (Java Language Specification) correctly refers to it as a remainder operator Modulus operator gives you the result in 'reduced residue system' For example for mod 5 there are 5 integers counted 0,1,2,3,4 In fact 19=12=5=2=9 (mod 7) The main difference that the answer is given by programming languages by 'reduced residue system'
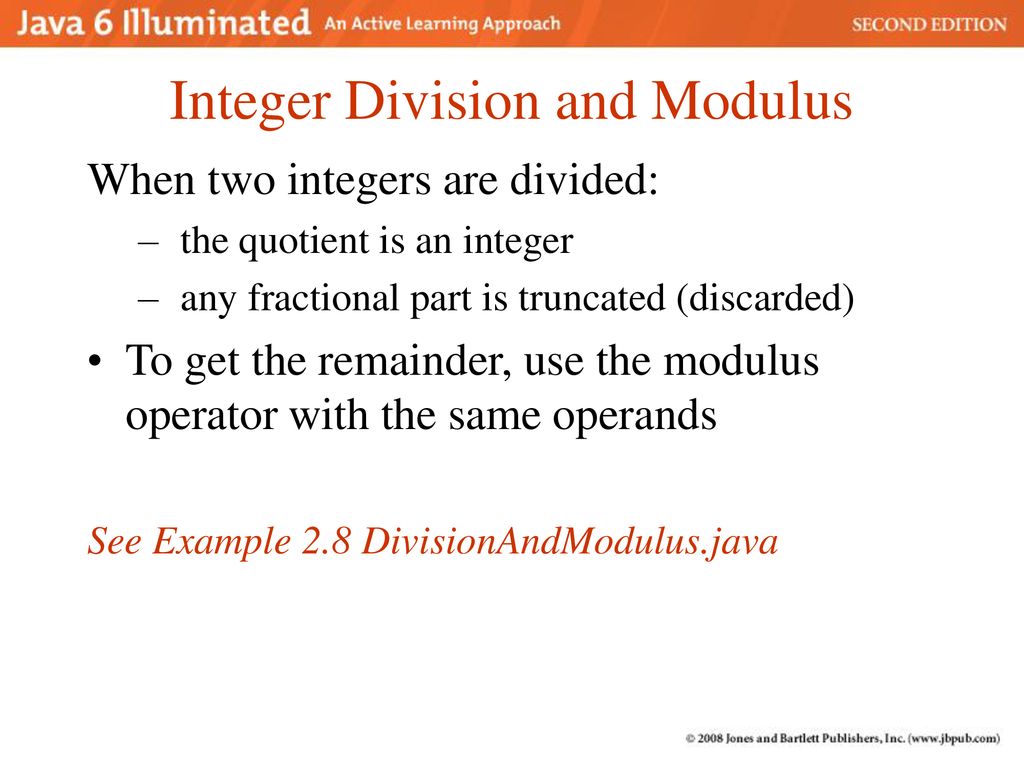



Programming Building Blocks Java Basics Ppt Download




What Is The Result Of In Python Stack Overflow
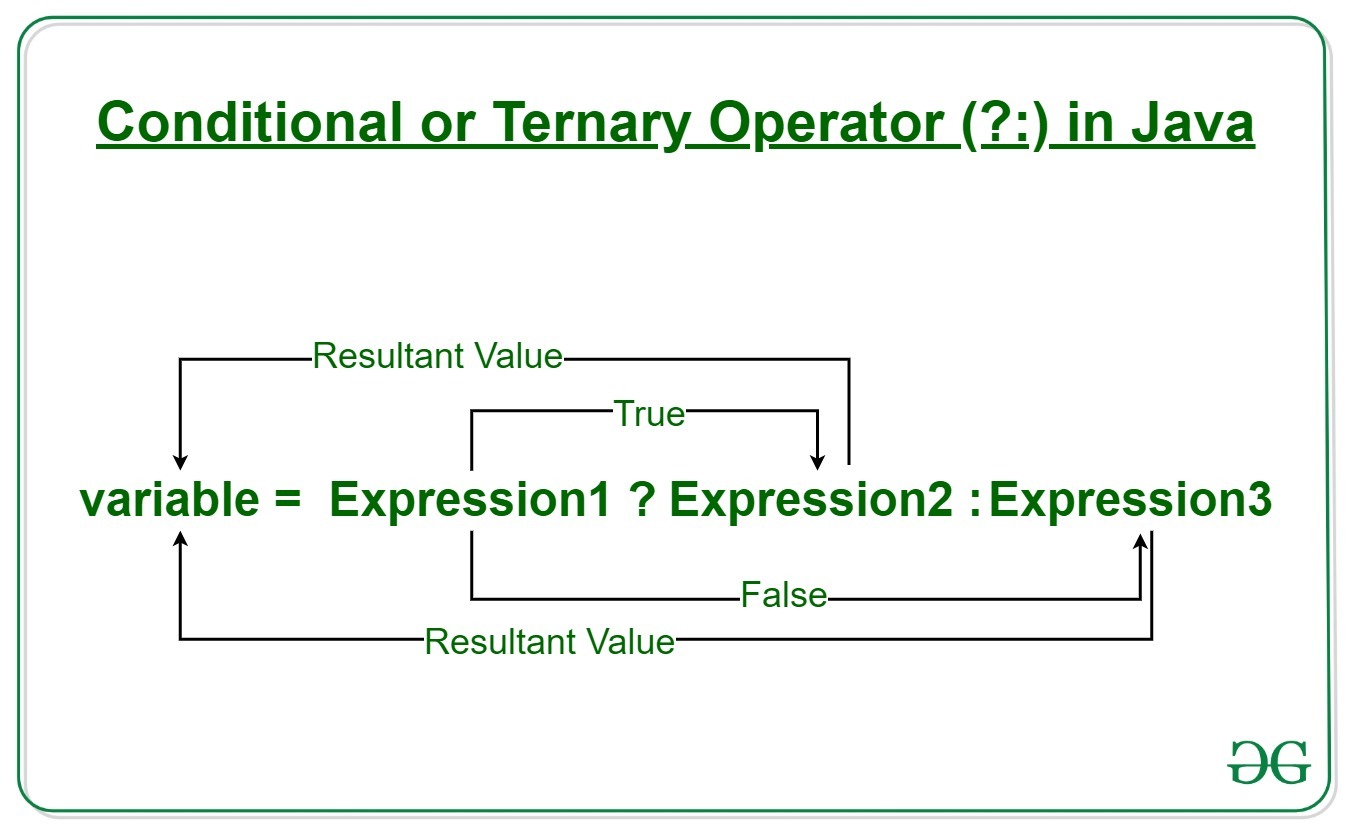
Modulo operation In computing, the modulo operation returns the remainder or signed remainder of a division, after one number is divided by another (called the modulus of the operation) Given two positive numbers a and n, a modulo n (abbreviated as a mod n) is the remainder of the Euclidean division of a by n, where a is the dividend and n isDivision and Modulo Operator ExplainedI am continuing on with my video series on Java programming for beginners In this video, we discuss Integer division aTernary Operator Java In Java, the ternary operator is a type of Java conditional operator In this section, we will discuss the ternary operator in Java with proper examples The meaning of ternary is composed of three parts The ternary operator (?



1
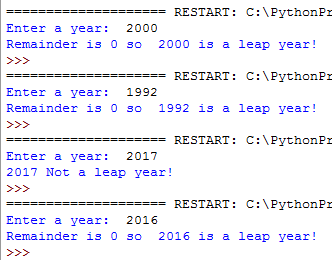



How Modulo Works In Python Explained With 6 Examples
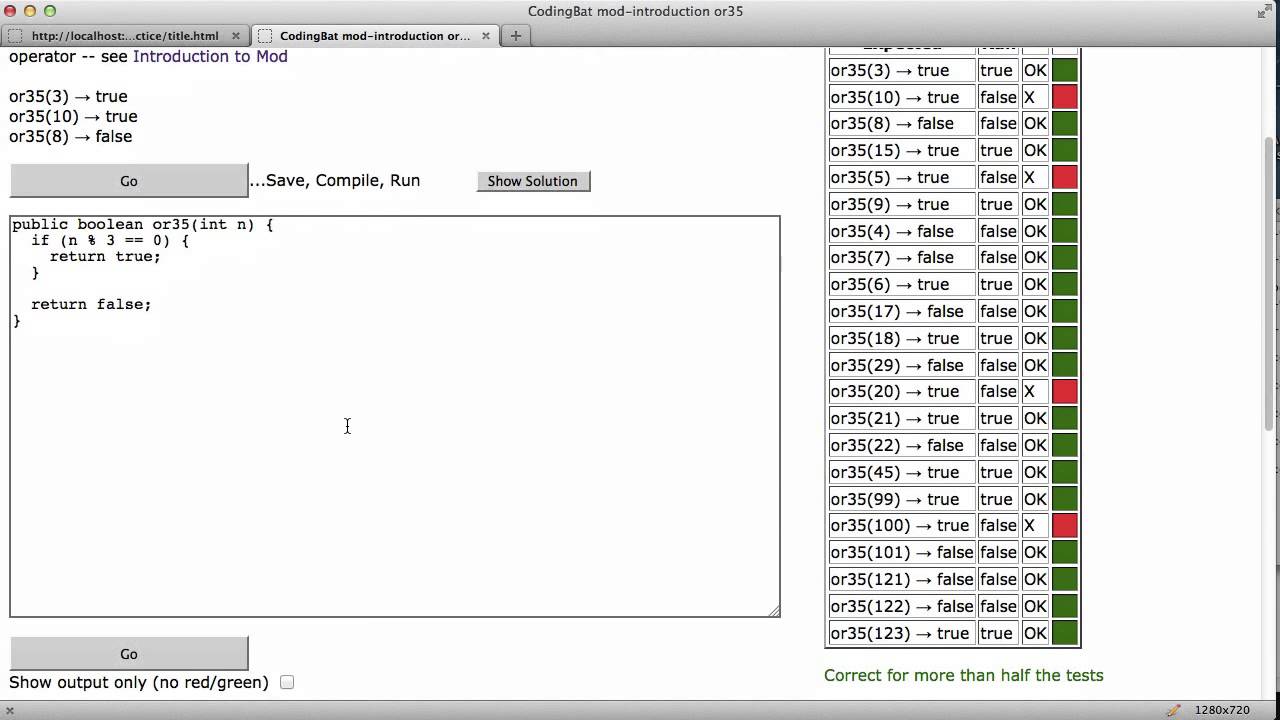
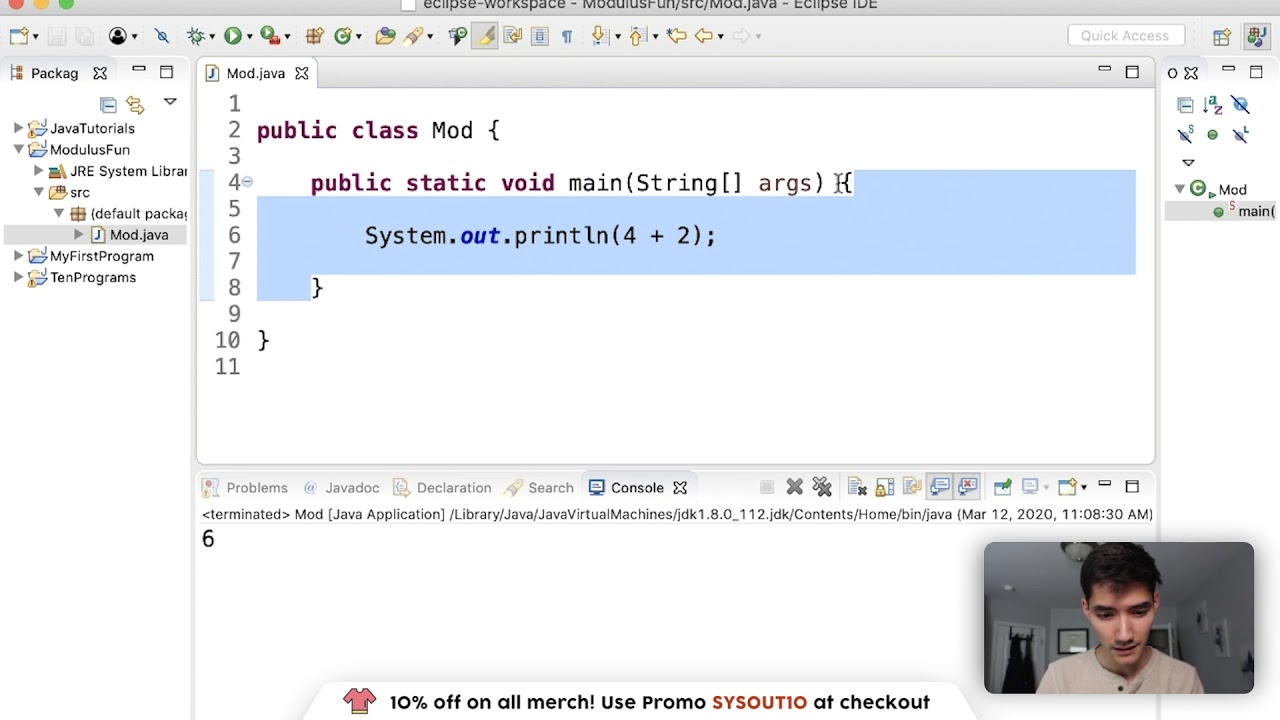
Java provides many types of operators which can be used according to the need They are classified based on the functionality they provide Some of the types are Arithmetic Operators Unary Operators Assignment Operator Relational Operators Logical Operators This example shows how to use Java modulus operator (%) */ public class ModulusOperatorExample { public static void main (String args) {System out println ("Java Modulus Operator example");The modulus operator (which we'll often call the mod operator) gets the remainder of a division




Java Modulus Operator Remainder Of Division Java Tutorial




Java Program To Check Even Or Odd Number
Java Operators Exercise 1 Exercise 2 Exercise 3 Exercise 4 Go to Java Operators Tutorial Java Strings Exercise 1 Exercise 2 Exercise 3 Exercise 4 Exercise 5 Exercise 6 Go to Java Strings Tutorial Java Math Exercise 1 Exercise 2 Exercise 3 Go to Java Math Tutorial Java Booleans The Modulus operator just gives you that remainder, so 9 % 3 = 0 and 10 % 3 = 1 Incidentally, you use modulus operations everyday, when you use a twelvehour clock after hitting twelve, the clock "warps around" to one Three o'clock PM Java allows you to combine assignment and addition operators using a shorthand operator For example, the preceding statement can be written as i =8;




Basic Operators In Java Geeksforgeeks




Java Modulus Operator Remainder Of Division Java Tutorial




Mod Division In Java Vertex Academy




The Modulo Operator Unplugged Cs Unplugged




Java Program To Check Even Or Odd Number




Bitwise Operators In Python Real Python




What S The Syntax For Mod In Java Stack Overflow




Modulus In Java Remainder Or Modulus Operator In Java Edureka




Mod Division In Java Vertex Academy




Modulus Or Modulo Division In C Programming Language Youtube



Modulo Problem In Java Dreamix Group



Arithmetic Operators In Java 7 Best Arithmetic Operators In Java




Modulus Operator In C C Javatpoint




Numbers In Python Real Python




The Ultimate Free Java Course Part 1



Introduction To Mod Code



Python Operator Types Of Operators In Python Dataflair



1



Java Modulus Operator Youtube



Cse13 Intermediate Programming Operators Conditionals Loop Ppt Download




Java Tutorial Division And Modulo Operator Explained Youtube




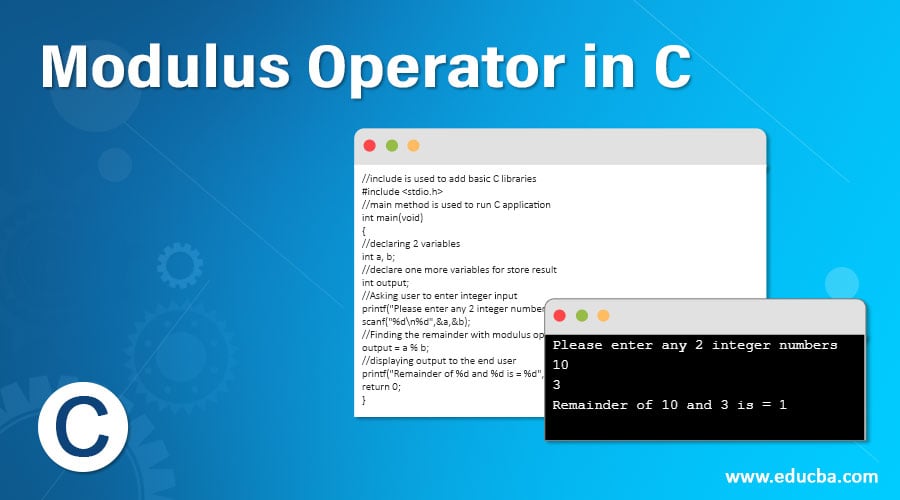
The C Modulus Operator Mycplus C And C Programming Resources




Arithmetic Operators In C Top 7 Arithmetic Operators In C



Operators And Variables




Java67 How To Use Modulo Modulus Or Remainder Operator In Java Example



Java Remainder Modulo Operator With Negative Numbers Programming Guide



Types Of Java Operators Nourish Your Fundamentals Dataflair




Java Arithmetic Operators Part 4 Modulus Operator With Integer Operands Youtube




How To Use Modulo In Python




Java Modulo Operator Modulus Operator In Java Journaldev




Basic Core Java Up To Operator




Operators In Java Programming Language Learn Java By Examples



Modulus Operator In C Calculations Working Of Modulus Operator



Java Modulus Operator Modulus Operator In Java



Java Operators Ternary Operator




Modulus In Java Remainder Or Modulus Operator In Java Edureka




Identifiers Symbolic Names Ppt Download



Java Programming Integer Division And The Modulus Operator The Seeker S Quill
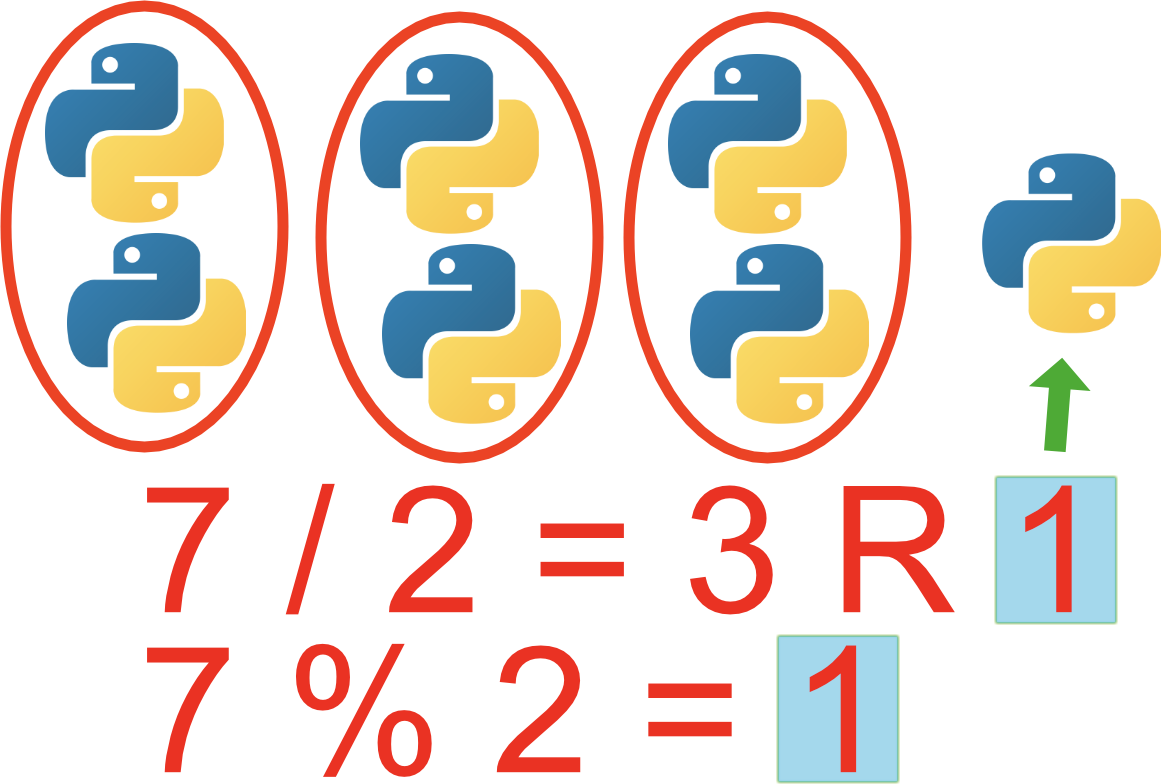



The Python Modulo Operator What Does The Symbol Mean In Python Solved




Arithmetic Operators In Java Coding River Mag



The Ultimate Free Java Course Part 1



The C Modulus Operator Mycplus C And C Programming Resources



The Ultimate Free Java Course Part 1



Types Of Java Operators Nourish Your Fundamentals Dataflair




How To Use Modulus Operator In Python




Sum Of First And Last Digits In Java




Programming In C Tutorial 5 The Modulus Operator Youtube
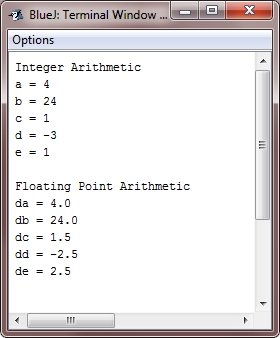



Java Arithmetic And Modulus Operator
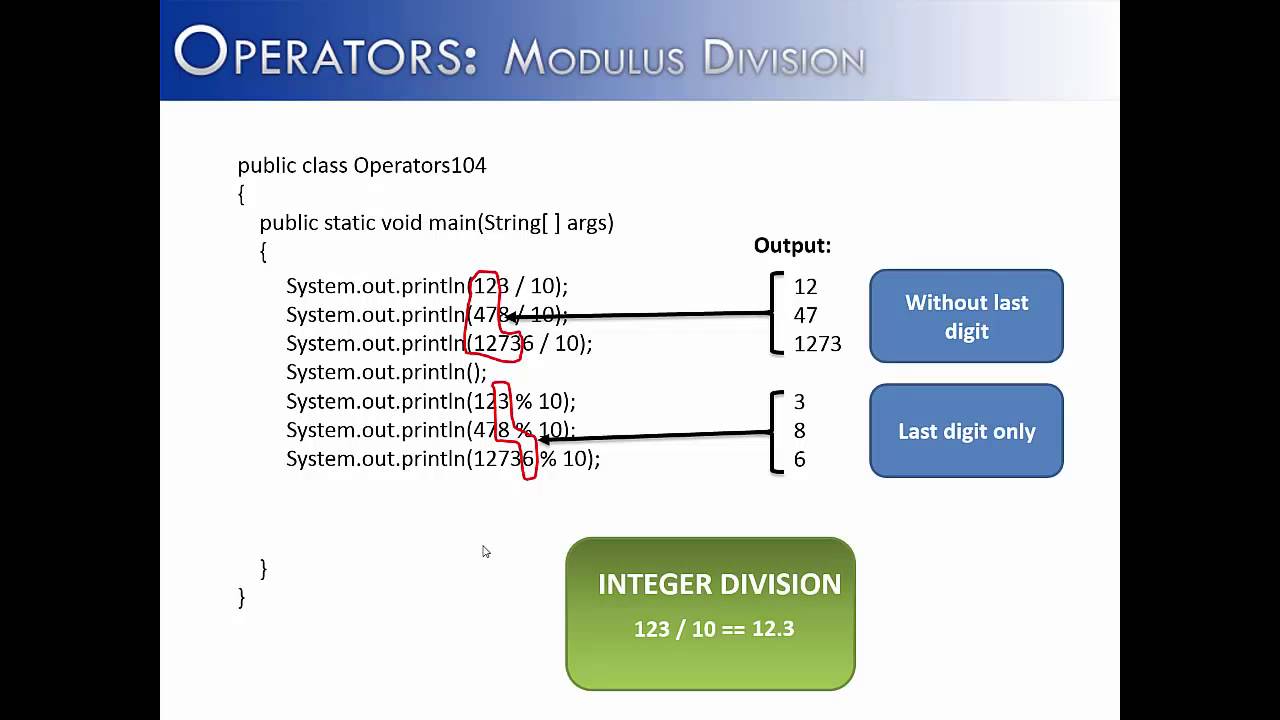



Operators Part 4 Modulus Division Java Youtube
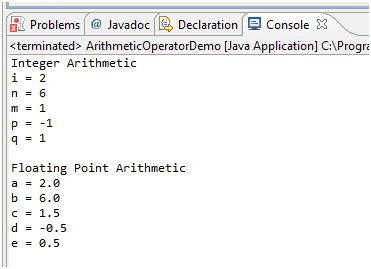



Java Arithmetic Operators W3resource




Unit 3 Javascript Introduction Java Script Is A




How To Use Modulus Operator In C
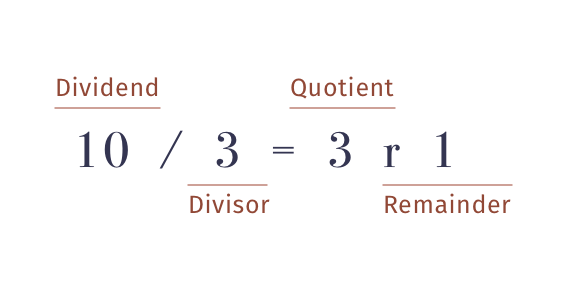



Python S Modulo Operator And Floor Division



Java Tutorial Division And Modulo Operator Explained Youtube




Mod Division In Java Vertex Academy




Modulus In Java Remainder Or Modulus Operator In Java Edureka



Modulo Operation Wikipedia



How Does The Modulus Operator Works Quora




Even Odd Program In Java Programming Simplified



Modulus In Java Remainder Or Modulus Operator In Java Edureka



Java Operators With Examples Java Tutorial



Java Ternary Operator With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Integer Division And Modulus Programming Fundamentals



Java Modulus Tutorial Learn Modulus In Java Youtube




Mod Division In Java Vertex Academy



1
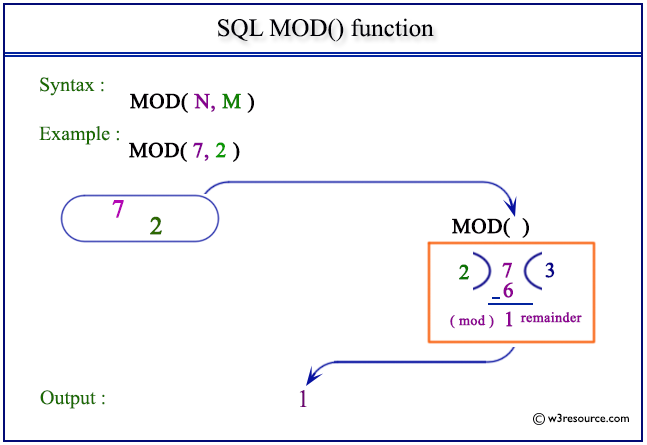



Sql Mod Function W3resource




Java A To Z With Java Jayan Java Modulus
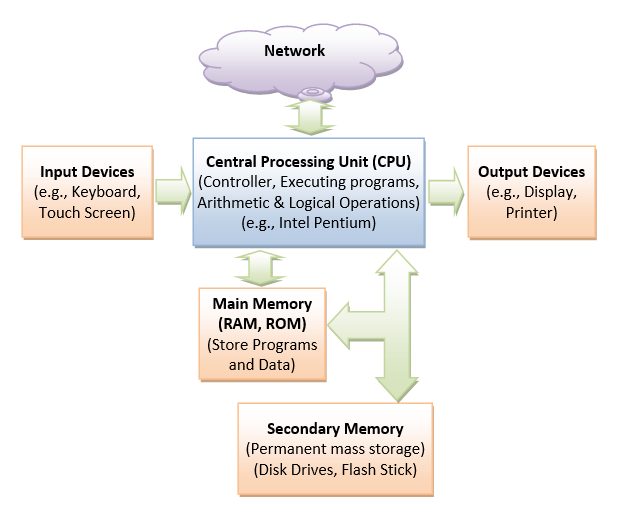



An Introduction To Java Programming For First Time Programmers Java Programming Tutorial
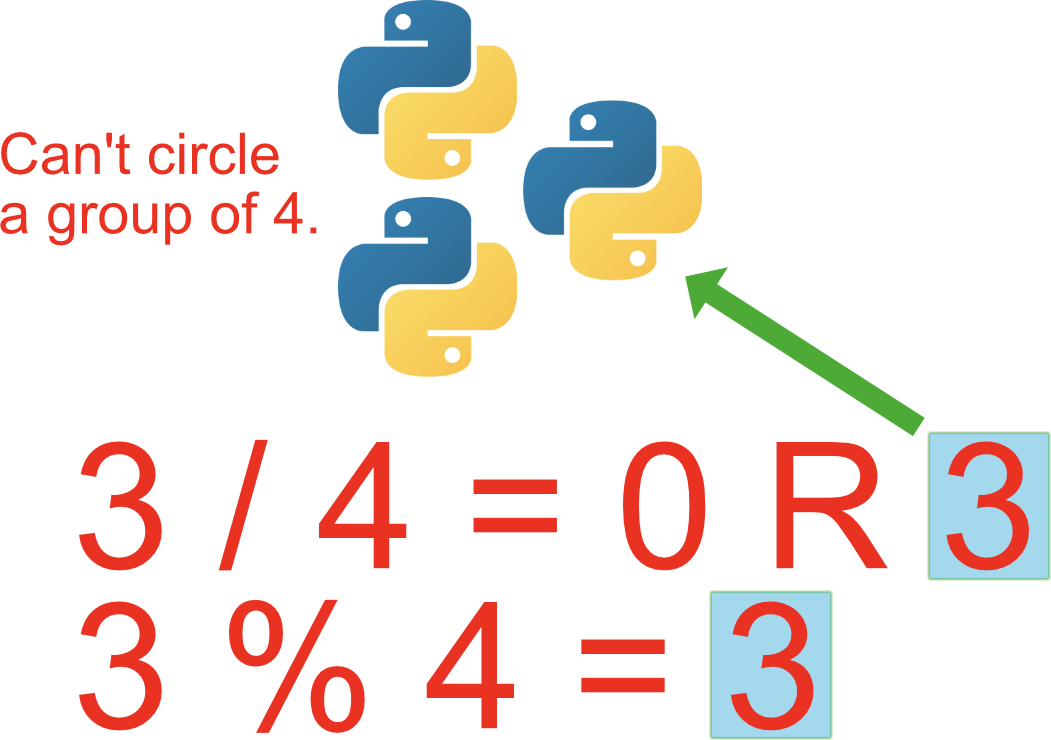



The Python Modulo Operator What Does The Symbol Mean In Python Solved




The Modulo Operator Unplugged Cs Unplugged




Hx28gwk8c Fyrm




Modulus In Java Remainder Or Modulus Operator In Java Edureka




C Programming How Does The Modulus Operator Work When We Divide A Smaller Number By A Larger Number For Example 3 5 Or 5 10 Quora




Arithmetic Operators In Java Laptrinhx




Python Operators Their Operation Symbols And Meaning



1




Engineered For Tomorrow Unit 1 Introduction To Java




Understanding The Modulus Operator Stack Overflow




Modulus Operator In C And C Hindi Urdu Youtube



Objective C Boolean Operators



011 Using Operators And Modulus Division In Java Youtube




Teaching Kids How To Code Using The Mod Operation Dummies




How To Use Modulus Operator In C



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿